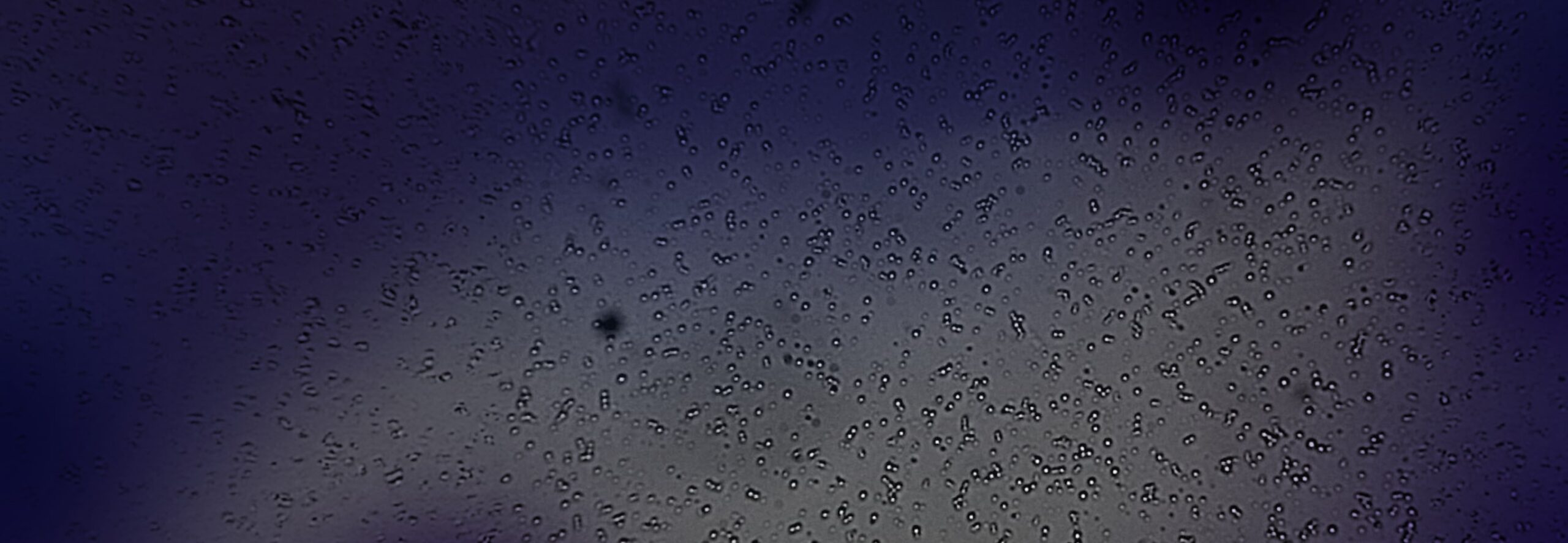
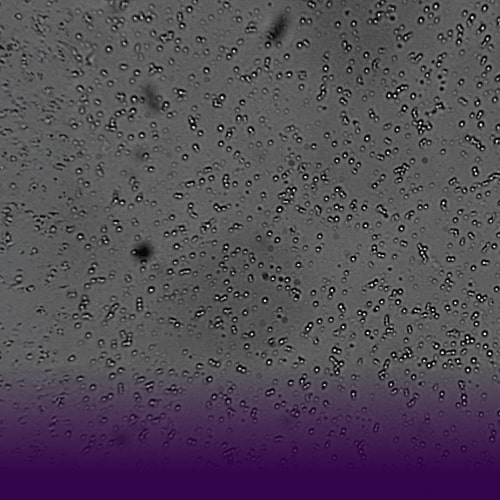
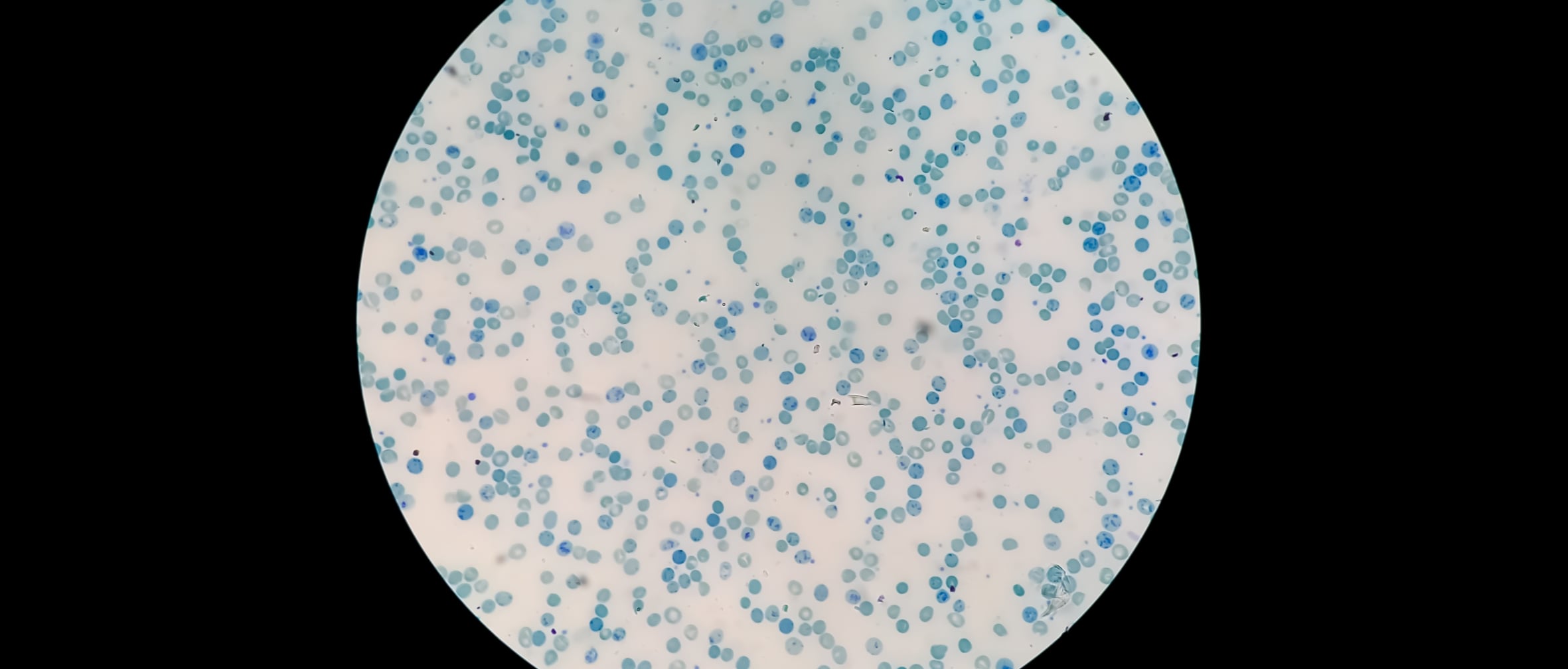
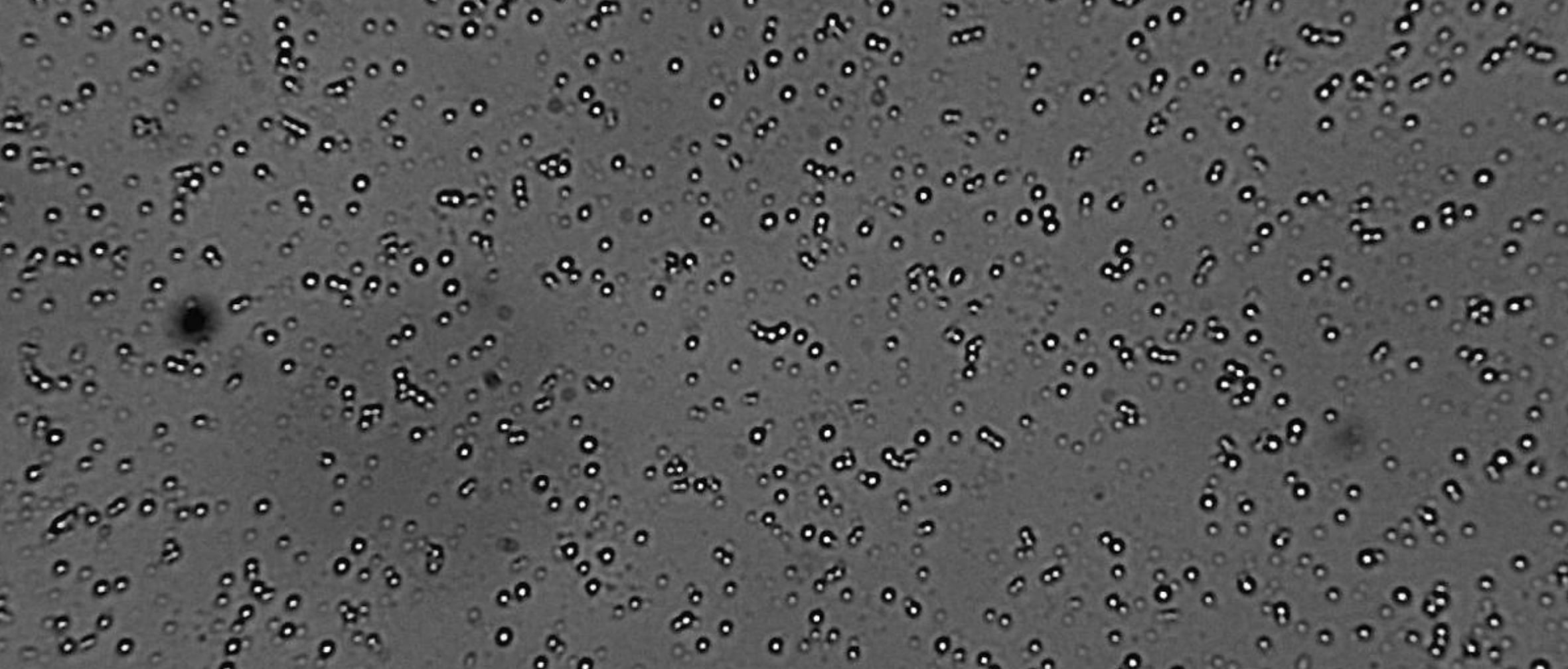
In semi-solid systems, smaller globule size enhances dispersion, supports faster drug release, and improves consistency across batches. When globules are uniformly sized and well-distributed, the risk of adverse effects, incomplete mixing, or uneven drug delivery is significantly reduced. Determining globule size also helps identify issues such as poor microstructure or uneven drug distribution, factors that affect both patient outcomes and product shelf life.
Changes in globules size over time may point to instability in emulsions, especially in formulations containing suspended actives. Visual analysis of these changes can reveal inconsistencies resulting from lot-to-lot differences or degradation during storage.