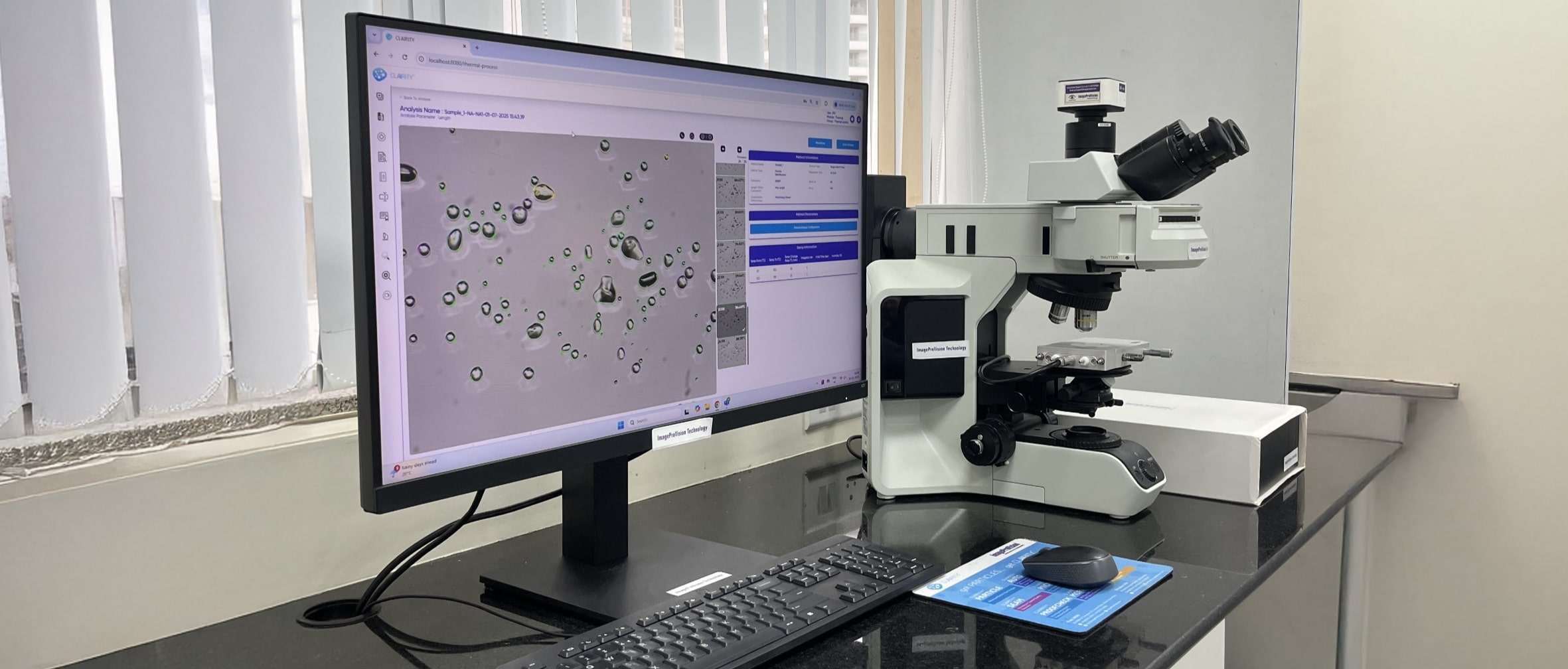
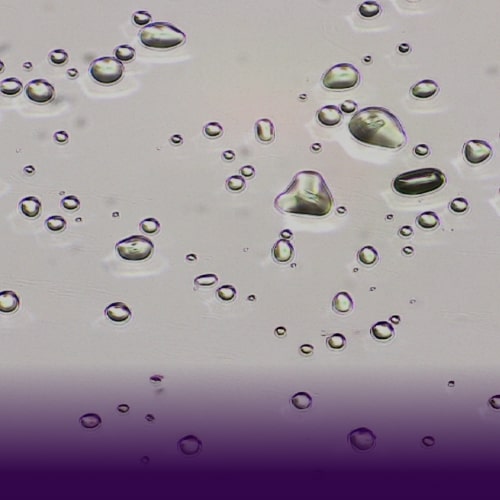
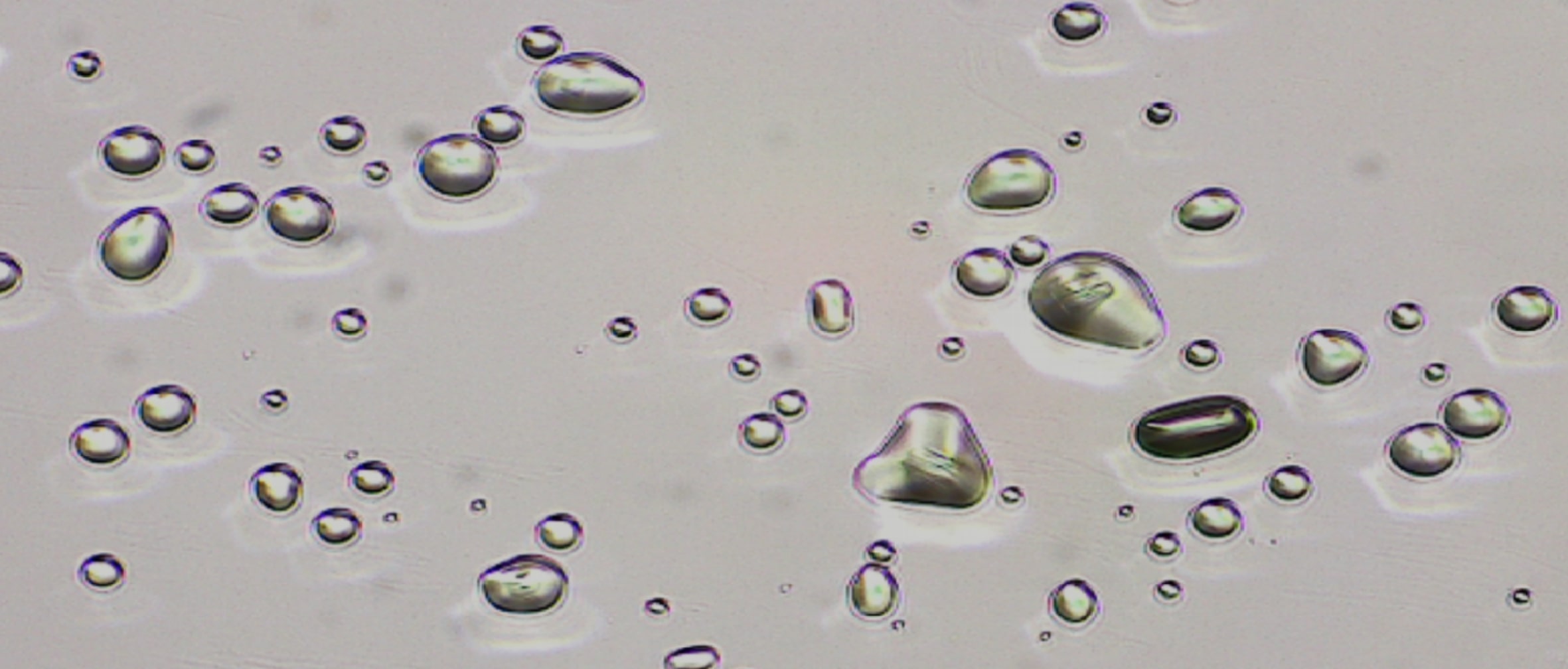
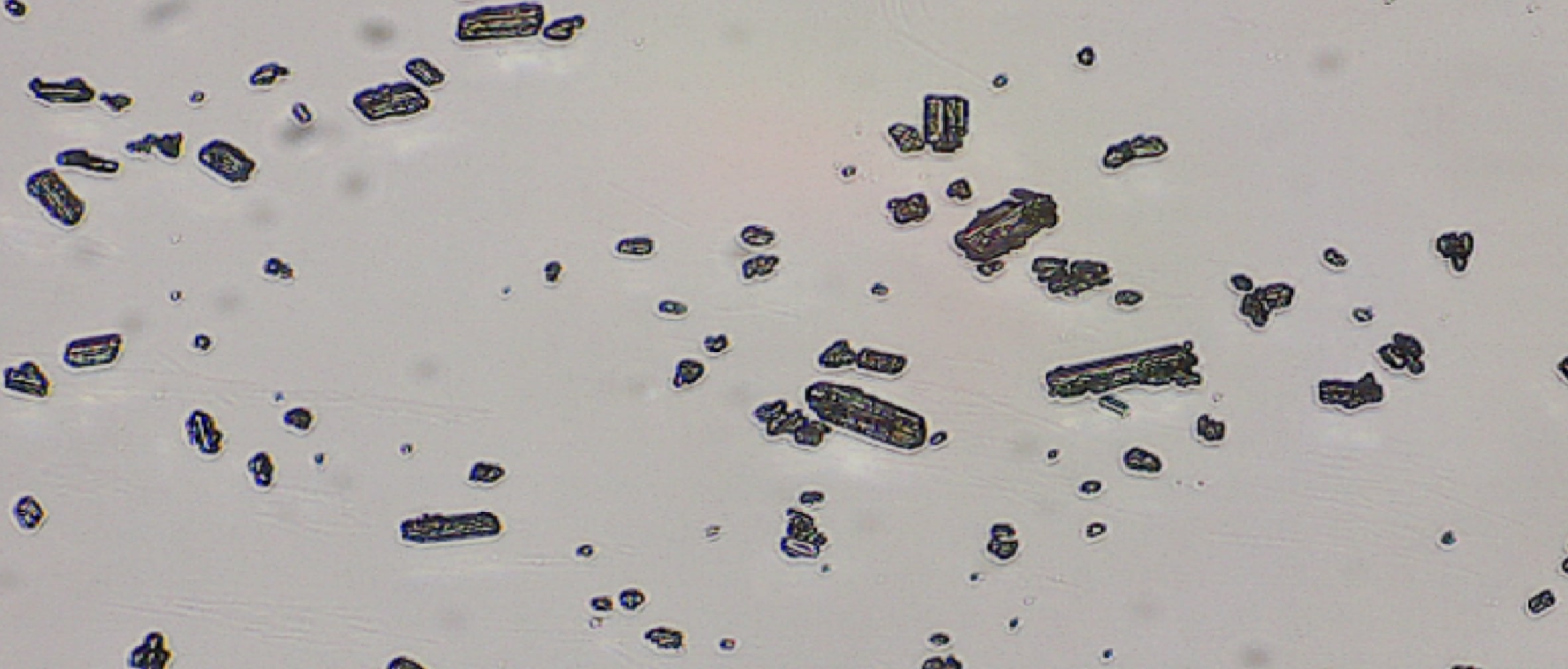
Precision imaging across diverse applications
See our Applications- API Particle Characterisation
- Capsule Seam Analysis
- Deformulation Analysis
- Excipient Particle Characterization
- Foreign Matter Inspection (Vial Inspection - Intrinsic & Extrinsic)
- Globule Size Determination in semi-solid dosage forms
- Hot Stage Microscopy
- Microbiology Colony Counting and Gram Staining
- Particulate Matter Count - Filter Paper Analysis