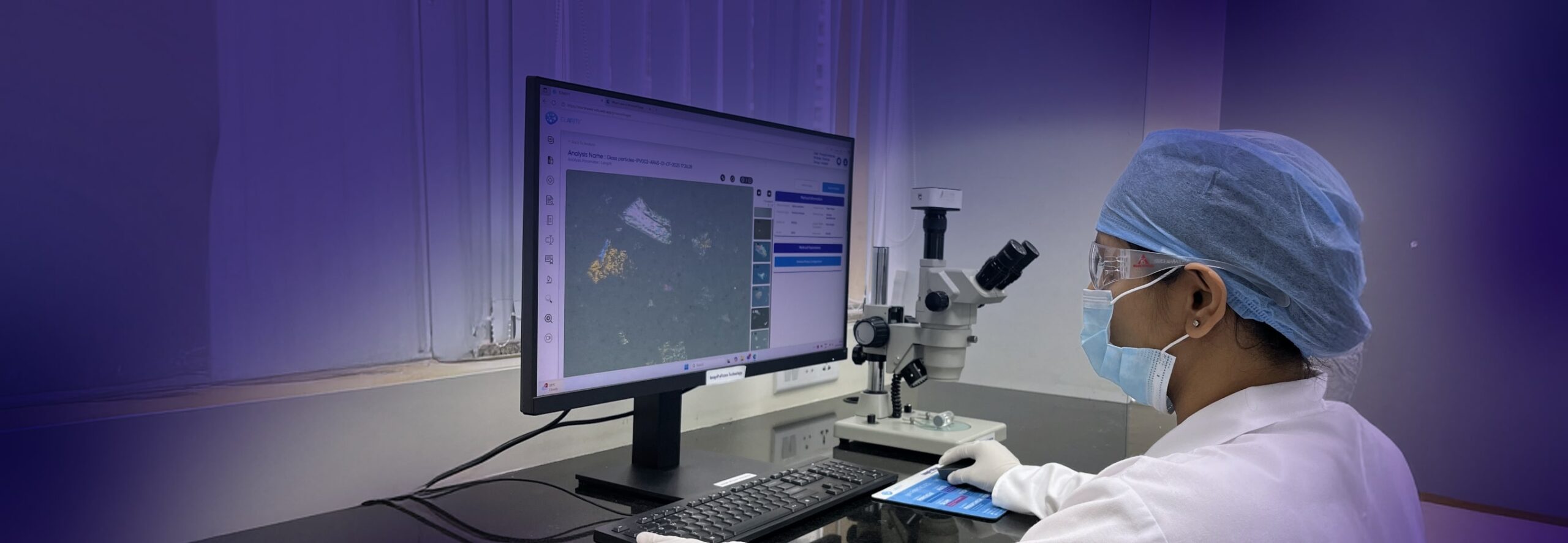
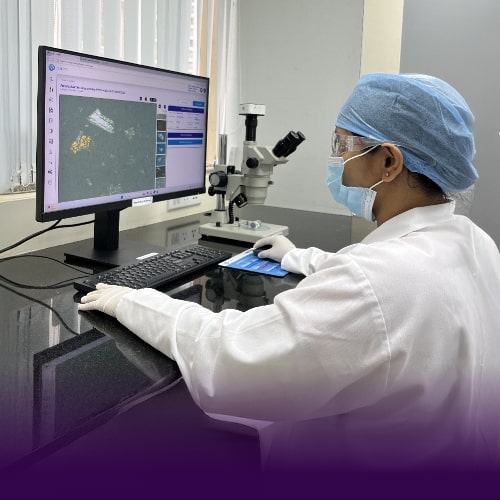
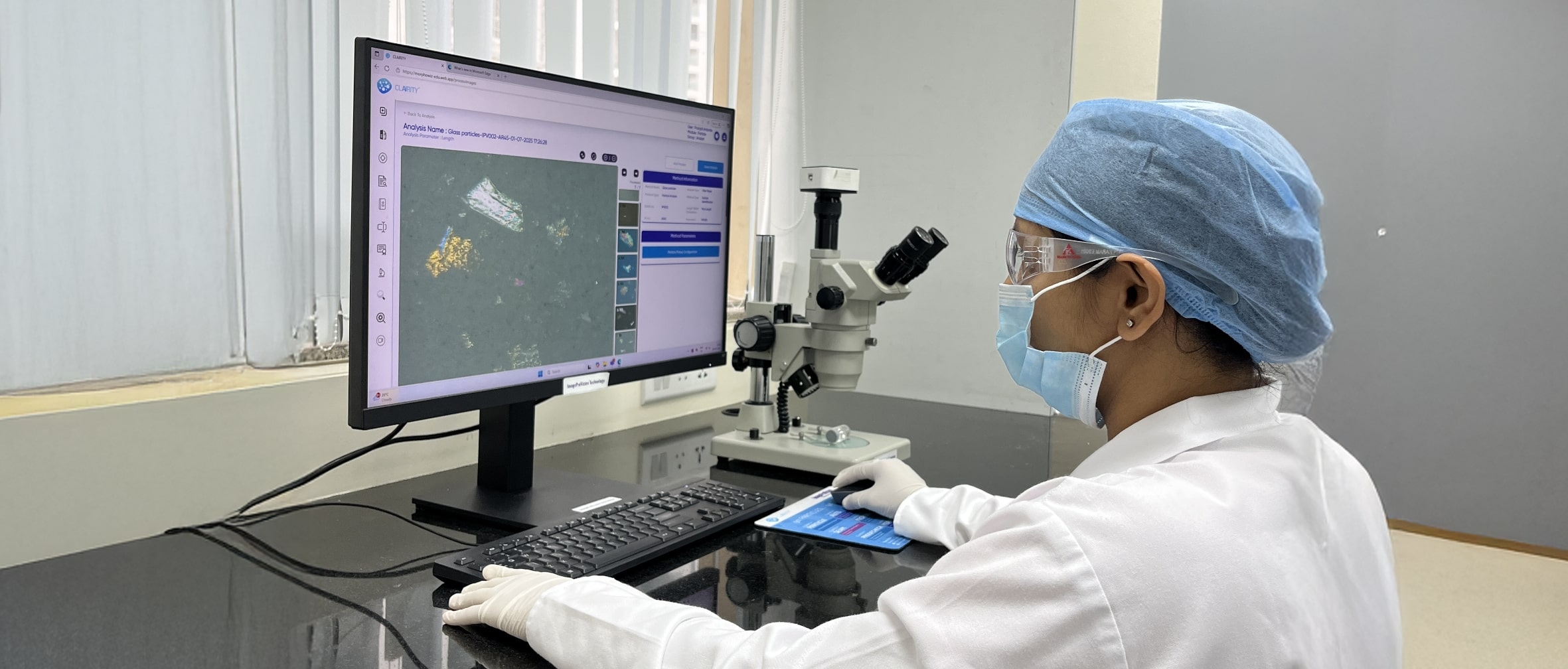
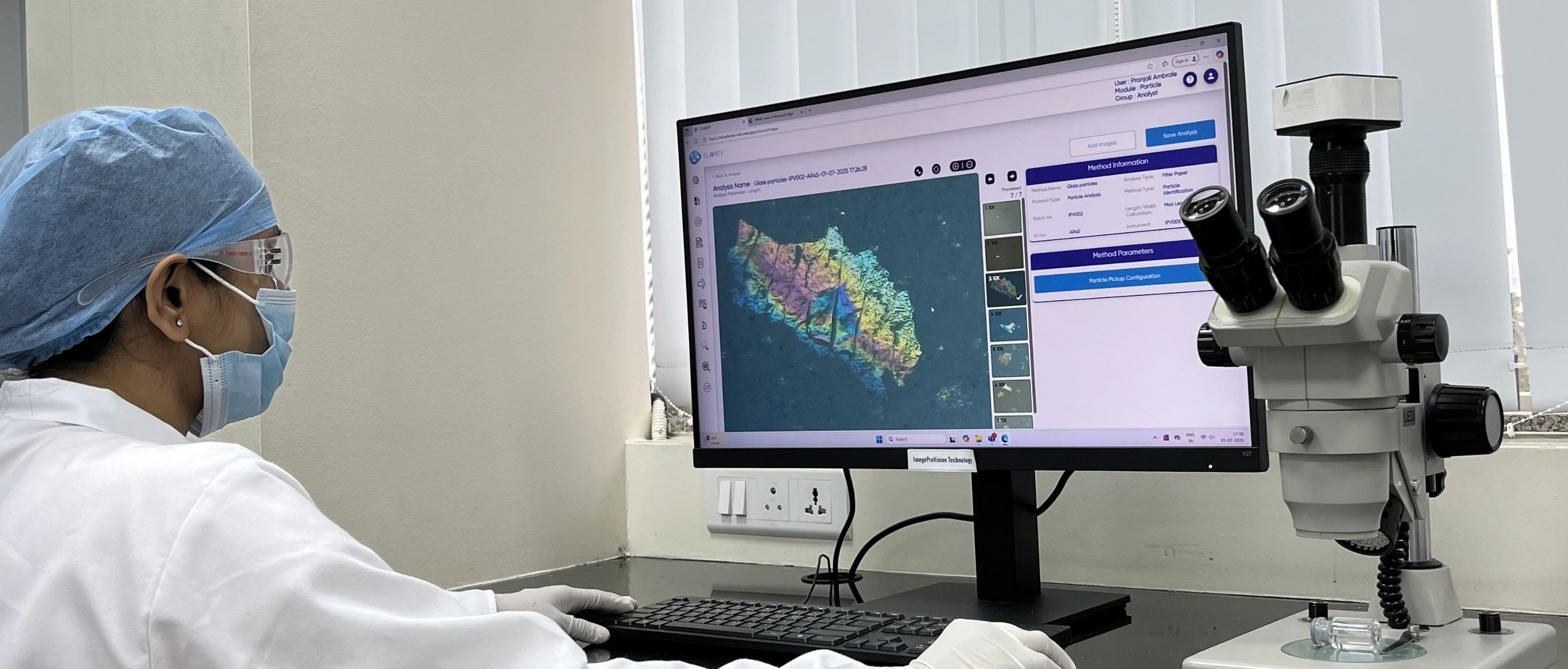
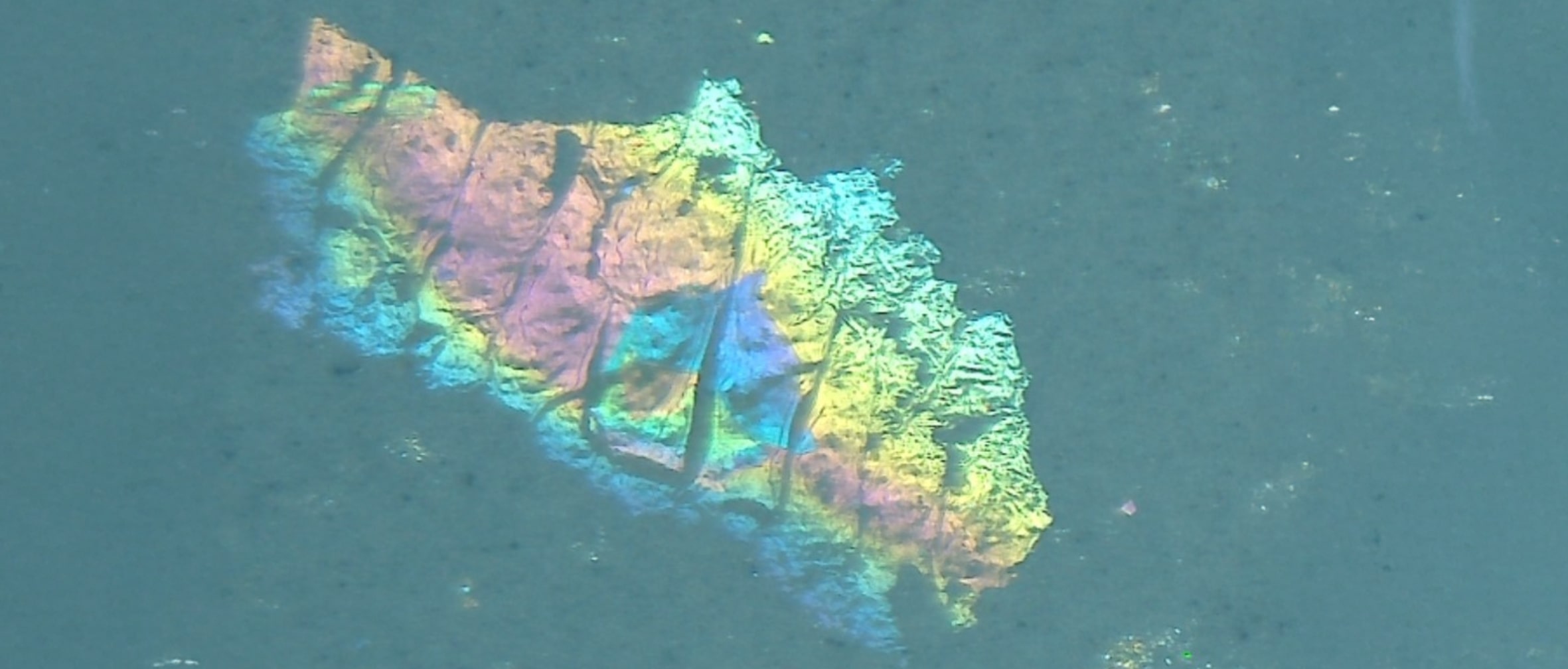
Extrinsic matter includes particles introduced from the external environment, such as dust, fibers, or debris, while intrinsic matter may originate from within the vial, including glass fragments, metal shavings, or process residues. Morphological analysis helps differentiate between these sources and determine the likely stage at which the contamination occurred.
Inherent particulates, including those from vial delamination or packaging components, are also examined as part of this process. Their shape, structure, and size provide vital clues to their source and potential impact on the formulation.